
Introduction
In 2023, U.S. consumers reported over $10 billion in losses to fraud, a 14% increase from the year prior, with phishing accounting for 75% of these losses. As digital banking expands, financial institutions face growing threats from sophisticated fraud techniques like identity theft and phishing. Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions are critical for combating these threats by implementing tools such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and real-time monitoring to detect unusual behavior, reduce fraud, and ensure regulatory compliance with standards like GDPR and PCI-DSS
The Rising Threat of Fraud in Finance
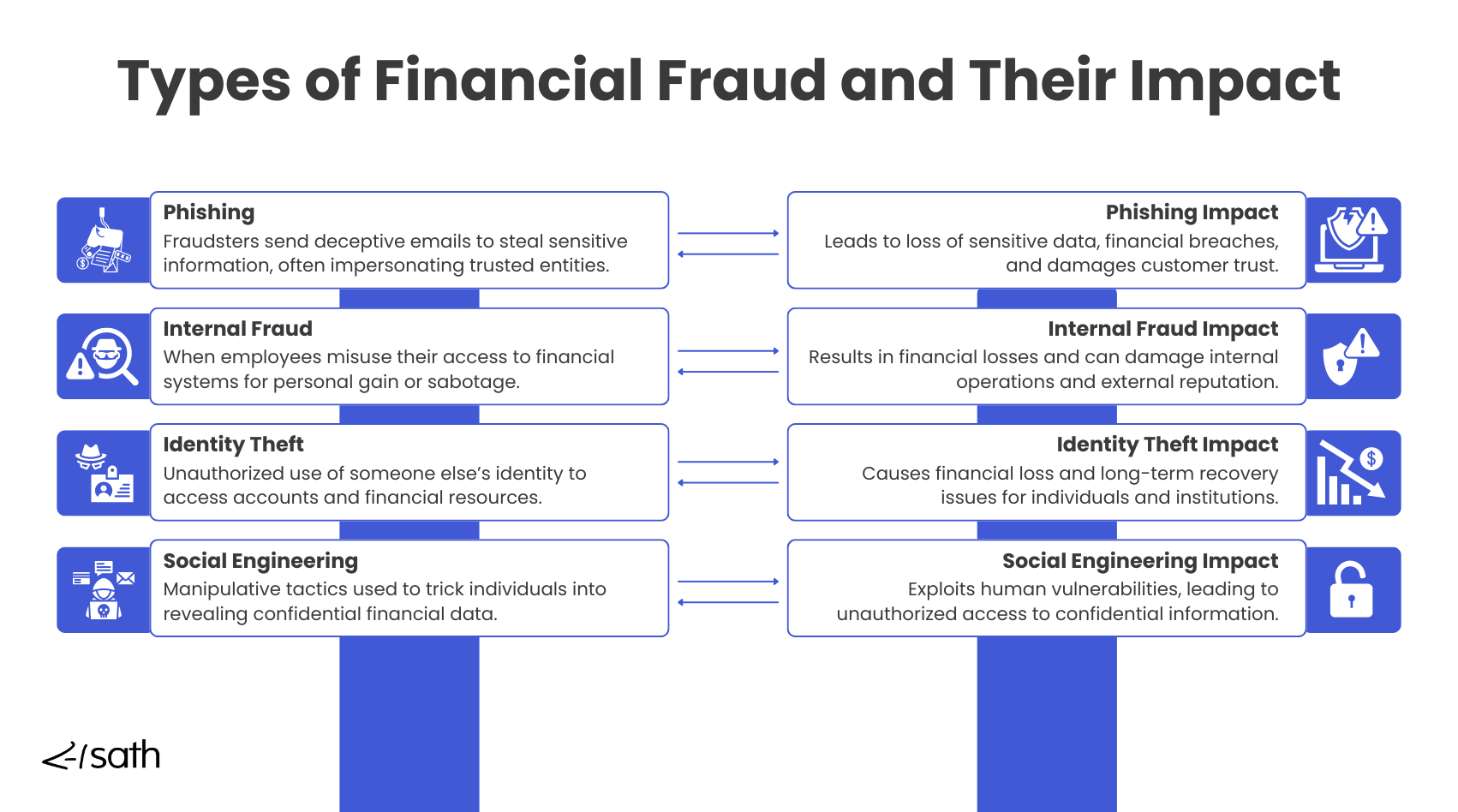
Financial fraud is becoming more advanced, creating serious challenges for institutions. Common types of fraud include internal fraud, where employees misuse their access for personal gain, and identity theft, where criminals use stolen credentials to pose as legitimate customers.
Phishing, where attackers trick people into revealing sensitive information, and social engineering, which relies on manipulating individuals to bypass security, are also widespread. These tactics are evolving rapidly, making it tough for financial institutions to stay protected.
The impact of fraud goes far beyond just financial losses. It can seriously damage a company's reputation, causing customers to lose trust. Financial institutions often face increased regulatory scrutiny after a fraud incident, which can lead to fines and added operational costs. Recovering from these breaches takes time and effort, affecting customer relationships and the institution's standing in the market.
As fraud techniques get more complex, traditional security measures struggle to keep up. More than simple passwords and basic access controls are needed to prevent these threats. Often, fraudulent activities aren’t detected until the damage is already done. That's why more advanced solutions, like Identity Access Management (IAM) for Finance, are so important. IAM offers real-time monitoring and smarter security that can quickly identify and respond to unusual behavior, providing better protection against modern fraud attempts.
Get our free info-graphic on how to prevent financial fraud!
Strengthening Authentication and Authorization to Prevent Fraud
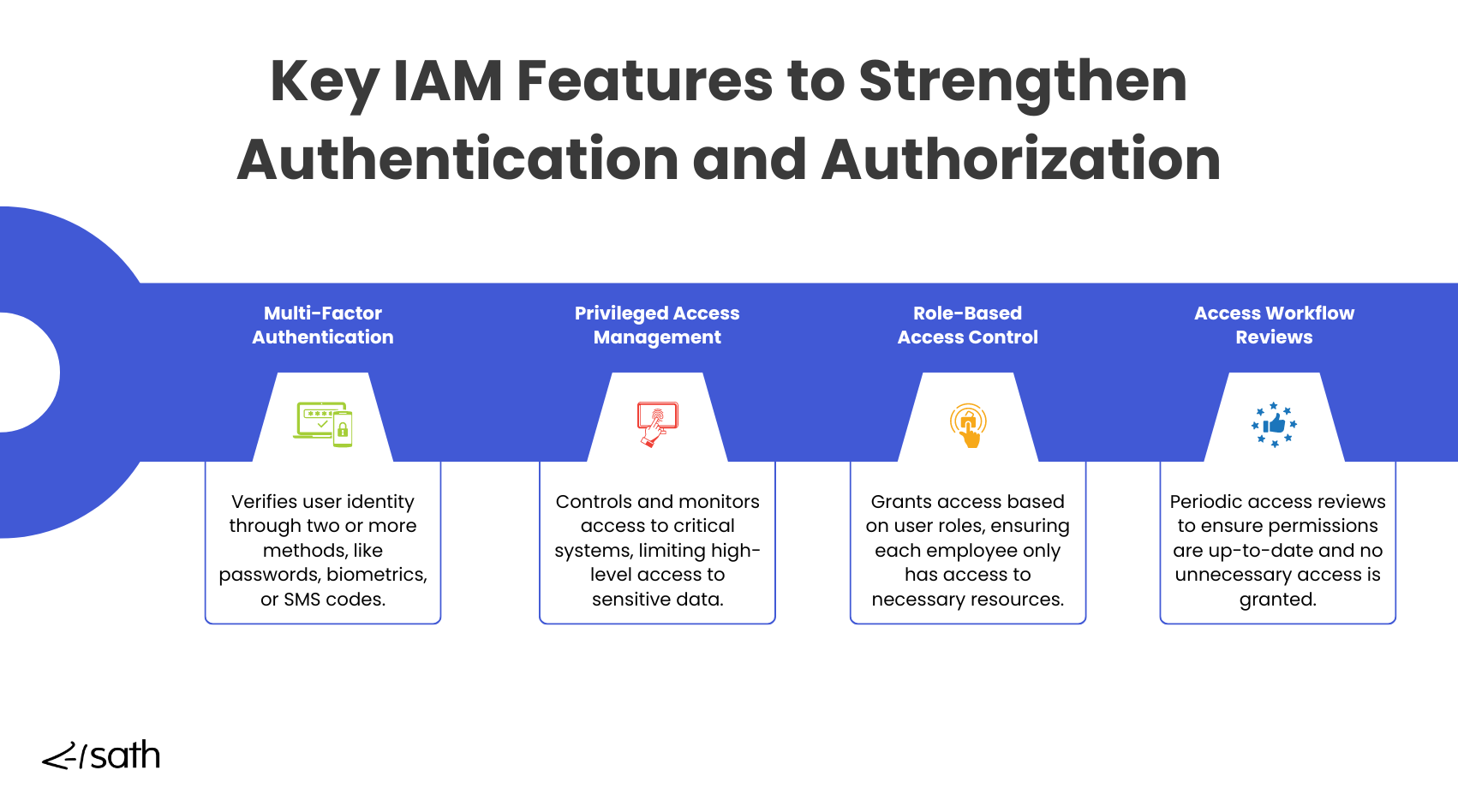
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide multiple pieces of evidence to verify their identity, such as a password and a code sent via SMS or generated by an app.
MFA is a critical tool in banking to prevent fraud by adding extra security layers when customers or employees access accounts, perform high-value transactions or log into sensitive financial systems. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised through phishing or social engineering attacks.
As part of a comprehensive IAM for Finance strategy, MFA strengthens both customer-facing and internal systems, protecting against a wide range of fraud attempts, particularly in online banking and mobile app access.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged Access Management (PAM) limits and controls access to critical financial systems and high-level administrative functions. In a banking environment, PAM is essential for securing access to systems that handle sensitive financial data, such as core banking platforms, payment gateways, and customer databases.
PAM prevents internal fraud by ensuring only authorized personnel, such as senior IT staff or auditors, access these sensitive areas. IAM for Finance helps prevent malicious insiders or external attackers from exploiting privileged access to commit fraud or breach critical financial systems by regularly monitoring and controlling privileged accounts.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) helps banks assign access rights based on an employee’s specific job function, ensuring they can only access the systems and data necessary for their role. This granular control reduces the risk of fraud by preventing unauthorized or over-privileged access to sensitive financial systems.
For example, a bank loan officer should only have access to customer loan applications and not to broader financial systems, reducing the risk of data misuse or fraud. Within an IAM for Finance strategy, RBAC simplifies managing access at scale, particularly in larger institutions, and helps minimize the risks associated with insider threats and human error.
Access Reviews
Access Reviews are practical tools for banks to regularly audit and adjust user permissions. Access needs can change frequently in financial institutions as employees move between departments or take on new responsibilities.
Automating access reviews allows banks to quickly identify and remove excessive or outdated permissions, which could otherwise be exploited in fraud attempts. For example, employees who no longer work in a certain department should have their access rights promptly revoked to prevent unauthorized access.
As part of the IAM for Finance framework, automating access workflow reviews reduces the risk of fraud by continuously aligning access rights with current roles, enhancing compliance and security.
Real-time User Behavior Monitoring
Real-time user behavior monitoring uses advanced analytics to track and detect unusual or suspicious activities, such as login attempts from unusual locations or transactions that deviate from normal patterns. In banking, this technology is crucial in detecting and stopping fraudulent activities before they cause significant damage.
For instance, if a bank detects an employee accessing sensitive financial data outside of normal working hours or from an unusual device, the IAM system can flag this as a potential fraud attempt and trigger an immediate response. Integrated into an IAM for Finance system, real-time monitoring provides an extra layer of protection, helping banks swiftly react to threats and prevent fraudulent transactions from being completed.
Reducing Insider Fraud Through IAM
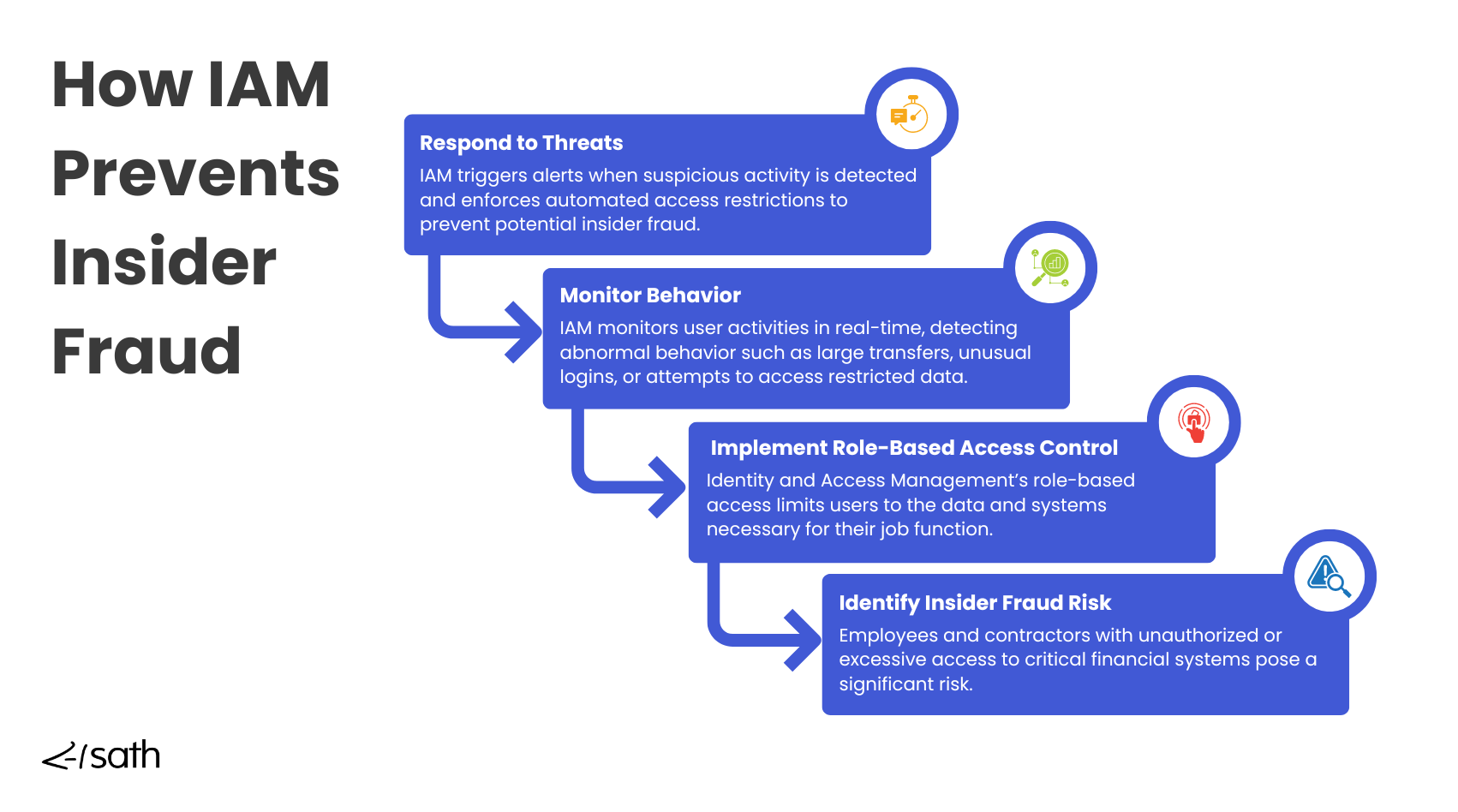
Insider fraud is a significant threat to financial institutions. Employees or contractors with authorized access can exploit their privileges for fraudulent activities, such as stealing customer data, manipulating financial records, or accessing confidential systems for personal gain.
Insider fraud is particularly dangerous because it comes from individuals with legitimate access to sensitive systems, making it harder to detect. For banks, insider threats can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) for Finance helps mitigate insider fraud by closely controlling and monitoring employee access based on roles and permissions. With IAM, access is granted only to the systems and data necessary for an employee’s specific role, minimizing the risk of over-privileged accounts.
For instance, a bank's customer service representative should only have access to customer inquiries, not high-level financial systems. IAM's role-based access control ensures that employees and contractors have limited permissions, reducing opportunities for internal fraud.
IAM for Finance also provides advanced monitoring tools to detect suspicious or unusual behavior from users accessing critical financial information. By tracking user activity in real time, IAM can identify anomalies such as irregular login locations, attempts to access restricted systems or unusual transaction patterns.
These alerts help banks respond quickly to insider fraud, limiting damage before it escalates. IAM’s ability to provide real-time visibility and monitor employee behavior is a powerful tool for preventing insider threats and reducing fraud risks within financial institutions.
Compliance and Regulatory Benefits of IAM in Finance
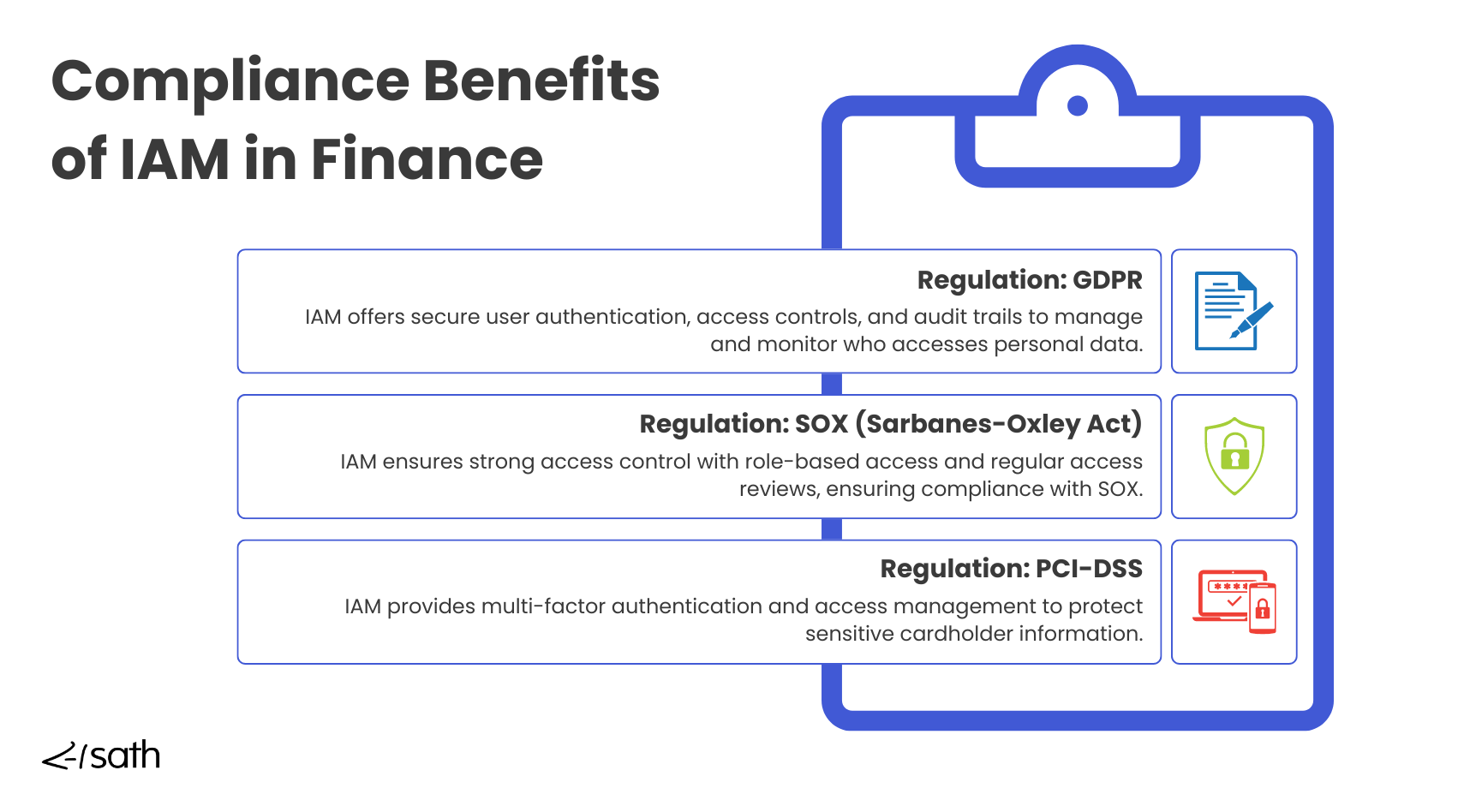
Banks and financial institutions must follow strict regulations like GDPR, SOX, and PCI-DSS to ensure that customer data is protected and access to critical financial systems is tightly controlled. These regulations help prevent fraud, protect sensitive information, and maintain the stability of financial systems. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, such as heavy fines, damaged reputations, and loss of customer trust.
Identity Access Management (IAM) for Finance is crucial in helping banks comply with these regulations. With IAM, banks can implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to secure customer accounts and internal systems, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive financial data.
IAM solutions also allow banks to manage privileged access to core banking platforms and payment systems, preventing unauthorized access to critical financial assets. Role-based access control (RBAC) further restricts access, so employees can only interact with the systems and data needed for their roles, reducing internal fraud risk.
One key regulatory benefit of IAM is the ability to generate detailed audit trails. In banking, this is especially important for compliance with regulations like SOX and PCI-DSS, which require detailed tracking of who accessed what data, when, and why. IAM solutions provide banks with clear records of user activities across their systems, making it easy to demonstrate compliance during audits and reduce operational risks. These audit trails help with regulatory reporting and provide visibility into potential security threats.
Long-term compliance brings several advantages to banks. Reducing fraud risks through well-managed access control helps protect customer data and the bank's reputation. Strong regulatory compliance also fosters better relationships with regulators, making it easier for banks to avoid penalties and maintain a smooth operational flow.
Additionally, customers are more likely to trust a fully compliant bank with data protection laws, which can lead to higher customer loyalty and a stronger position in the competitive financial sector. IAM for Finance is essential for ensuring banks meet these regulatory requirements while protecting themselves from fraud.
Conclusion
IAM for Finance helps banks protect against fraud and meet important regulatory requirements. IAM reduces risks by improving security with multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and real-time monitoring and provides the necessary audit records. A strong IAM system builds trust with regulators and customers, helping keep your bank secure. Want to learn more? Contact us today to see how our Sath can protect your bank from fraud and ensure compliance.
Continue to Part 6 in this Finance Series: Securing The Future Of Finance