IAM Reconciliation
Identity and Access Management (IAM) reconciliation is an important security process that ensures the accuracy, completeness, and validity of user access rights and privileges in a given system. It involves verifying access rights are assigned to the right users, and consistent with their roles, responsibilities, and the principle of least privilege.
By monitoring and comparing user accounts against authoritative sources such as directories, databases, or logs, IAM reconciliation helps to detect discrepancies which can be addressed quickly to prevent potential security threats.
What is data synchronization?
Data synchronization for IAM ensures consistent and up-to-date user identity and access information across diverse systems, applications, and directories within an organization.
This process streamlines the management of user data, enhances security, and supports seamless access control in complex IT environments.
IDHub Sync
Data Synchronization
Directional Sync
IDHub has Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC) process of synchronizing the attributes used for access control decisions across multiple systems or applications.
Stale Check
IDHub has an advanced feature for Data sync where stale days are configurations in each application which can be used to keep data in the system for a while upon deletion request.
Thresholds in Deletions
IDHub perform deletions of accounts and entitlements based on Thresholds set as configuration in applications to avoid accidental data wipe and data changes.
Sync Scheduler
IDHub Scheduler helps sync entire application data with IDHub on a timely manner. It pulls all the information and updates accounts and entitlement.
Process Synchronization
Every synchronization happens based on two keys:
- Recon Key
- Unique Field Key
These two keys are required for application onboarding, as well as the syncing process.
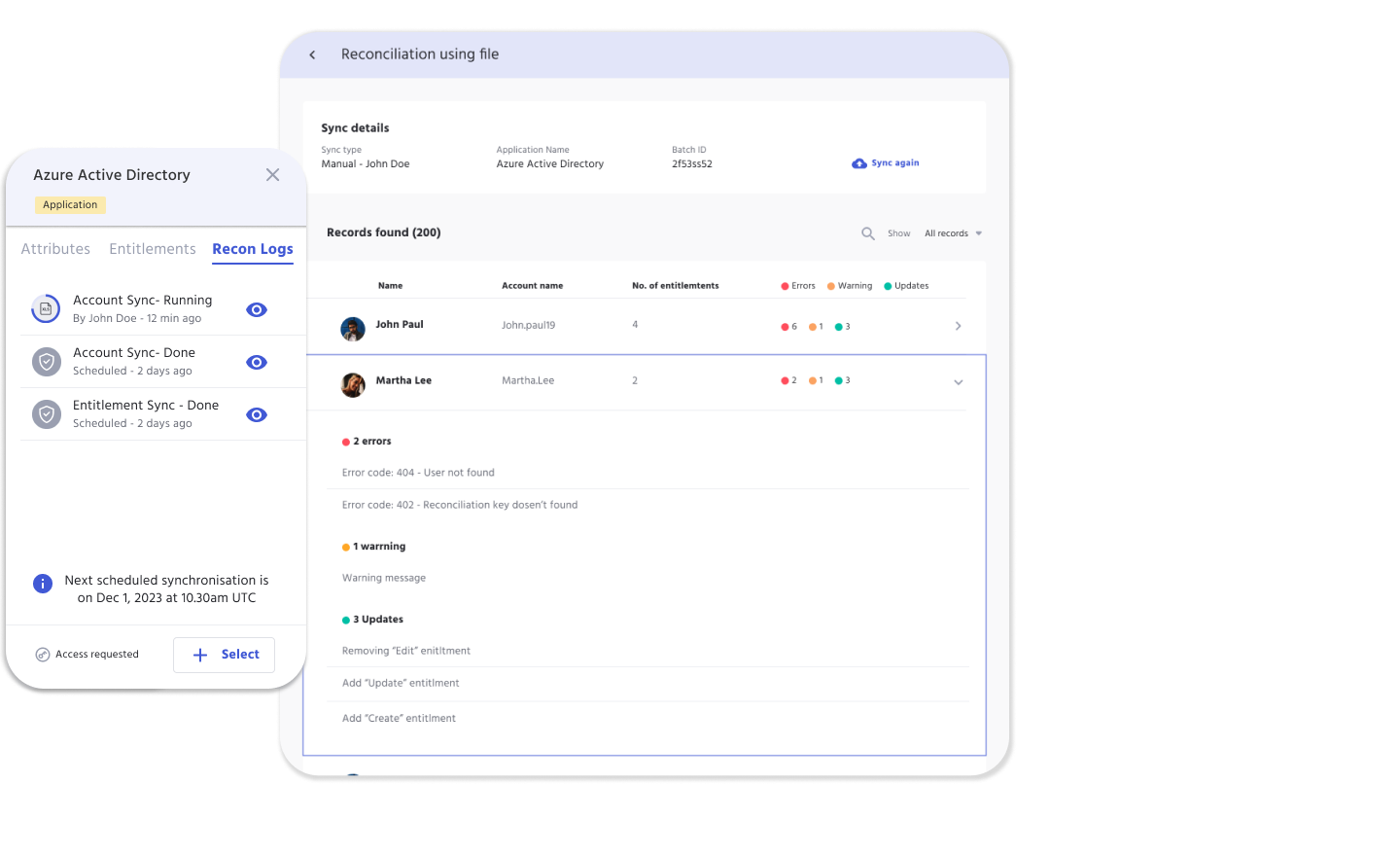
The Recon Key is directly related to the reconciliation feature in IDHub, and is a critical part when entering data into the spreadsheet.
For example: if the user name is the Recon Key, then the user name should match exactly on the spreadsheet, compared to what is in IDHub.
Reconciliation Process
- IDHub identifies whether the application is Trusted or Not-Trusted
- Trusted Application: used to pull user information into IDHub
- Non-Trusted Application: used to pull only account and entitlement related information into IDHub
- Account matching is done by the Unique Field Key
- User matching is done by the Recon Key
- When Accounts are matched:
- Each account attribute goes through Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC) and based on sync direction account attributes are updated in IDHub
- Each entitlement present in the target system is replaced with what is present in IDHub user account
- When account is not found in target system:
- Account goes into stale check process and waits for the account to become stale
- Once account is stale it is deleted from IDHub
- Thresholds:
- Deletions of accounts are prevented by threshold configurations in applications
- Once crossed the sync process is stopped to avoid accidental deletions
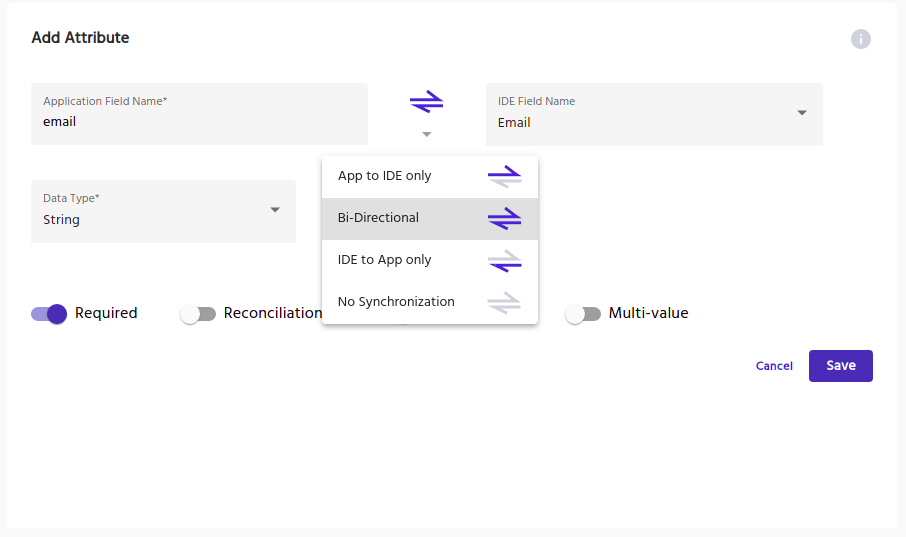
Attribute-Based Synchronization
Attribute-based synchronization is a unique feature used to sync data within IDHub and connected applications.
If there are any attribute data discrepancies found between the two, this feature allows organizations to determine whether IDHub or the application will override the alternate data.
Multiple syncing options are available upon configuration:
- IDHub to App
- App to IDHub
- Bi-directional Sync
- No Synchronization
Any attribute difference will be automatically synced, according to the configuration applied.
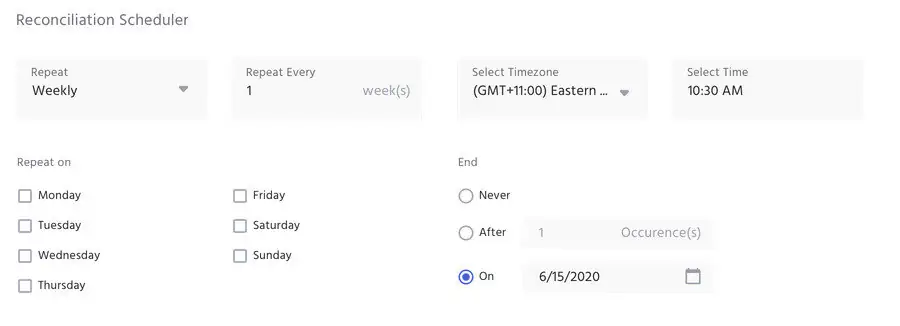
Synchronization Scheduler
The process for reconciliation or synchronization of data from target system to IDHub is called App Synchronization. It can be done in two ways:
- Manual Synchronization - This can be initiated upon request by administrators of IDHub
- Sync Schedules - This can be setup while application onboarding using IDHub wizard.
Connector Sync Methods
Real time synchronizations vary from connected apps. While selecting between options, IDHub development considers the specific requirements of a client's use case, including the desired level of real-time updates, scalability, efficiency, and integration capabilities of existing systems.
Examples:
- Entra ID (Formerly Azure Active Directory) Connector uses Change Feed
- Atlassian Connector uses Webhooks
Below are examples of additional event trigger technology:
Streaming
Event-Driven Architectures
Events represent significant changes or actions in the system, and they can be processed and distributed asynchronously. IDHub achieves real-time updates by publishing and consuming events through message brokers or event streaming platforms like Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ, or AWS EventBridge.
Real-time
Real-Time Databases
IDHub uses change data capture (CDC) method or streaming data pipelines to capture and propagate data changes in real time. IDHub uses Apache Kafka, Apache Pulsar, Firebase Realtime Database, and Amazon DynamoDB Streams.
HTTP
Webhooks
Webhooks are a mechanism for sending HTTP requests from one application to another in response to specific events or updates. They allow systems to notify and trigger actions in real time. By configuring webhooks, you can have your application receive immediate updates from external systems or services when specific events occur
Chat App
WebSockets
WebSockets is a communication protocol that enables real-time bidirectional communication between a client and a server. It provides a persistent connection that allows for efficient and low-latency data updates. WebSockets are well-suited for applications that require instant and frequent updates, such as chat applications, real-time collaboration tools, or live data streaming.
Feeds
Server-Sent Events
SSE is a unidirectional communication protocol that allows servers to send real-time updates to clients over HTTP. It establishes a long-lived connection between the client and the server, enabling the server to push data updates to the client as they occur. SSE is useful for scenarios where real-time updates from the server to the client are required, such as news feeds or real-time dashboards.
Messages
Push Notifications
Push notifications are a common mechanism used to deliver real-time updates to mobile devices or web browsers. They involve the server sending notifications to specific devices or browsers using platform-specific APIs. Push notifications are effective for scenarios where you need to notify users about important events or updates even when the application is not actively open.
File Based Synchronization
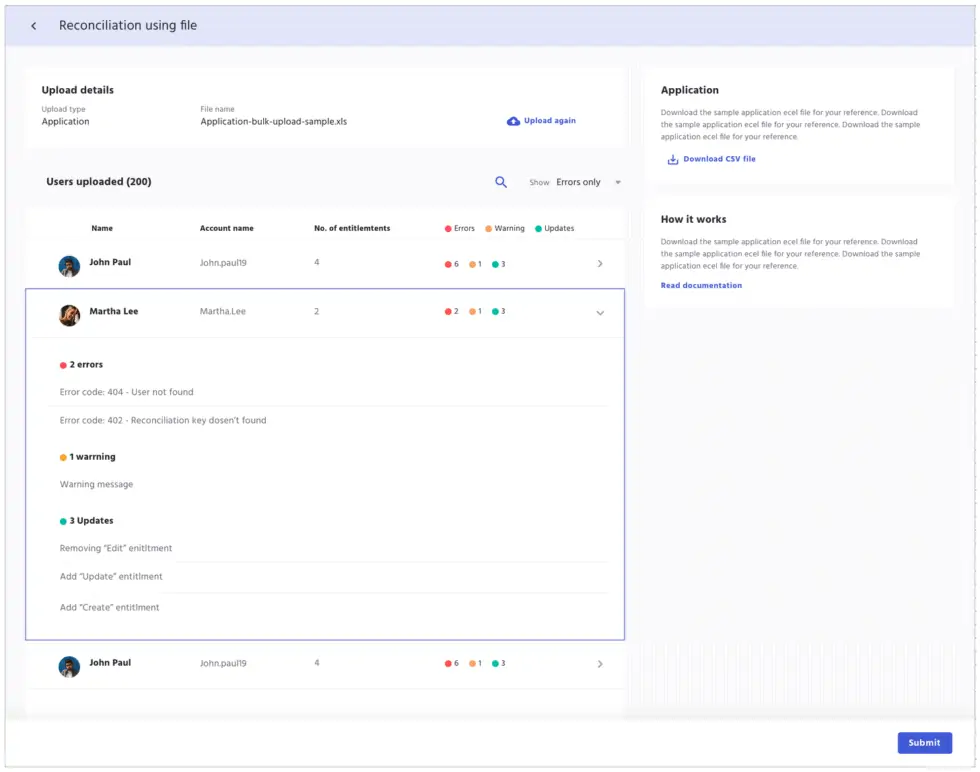
In IDHub, reconciling disconnected applications is done manually.
Admins will upload a delimited text file, allowing for quick processing of accounts, which can be used during the Certification process.
The synchronization process via a file upload allows the system to recognize the application so that IDHub can verify the access to resources update the access information accordingly.
This allows admins to easily identify access issues and make updates according to access management policies.
Compliance Tools for Cyber Security
Cyber Security Tools

Cybersecurity Assessment Template
Discover why cybersecurity assessments are vital for regulated industries—plus a free template to strengthen security, manage risk, and stay compliant.
Customizable Approval Workflow Templates
Download our most common Workflow Templates, including editable versions in Visio, SVG, and PDF formats. Completely free to you.

Application Onboarding Checklist
Learn about Application Onboarding essentials, and grab a copy of our free Google form, 36 question, application onboarding questionnaire to customize!