Why Use Elasticsearch Monitoring?
In this document, we will explore Elasticsearch, its applications, and the advantages it offers.
What Is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is a distributed, scalable, and available open-source search service based on Apache Lucene. It can be used to index and search large volumes of data quickly, analyze that data in near real-time, and return answers to queries in milliseconds. It can respond to search queries quickly because it doesn't search text directly; rather, it searches an index. Therefore, it is a powerful document-oriented search engine software tool, which uses a structured data format for storing and searching data. It also comes with extensive APIs for storing and querying data.
Why Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch enables rapid data retrieval, ensuring quick access to product information and analytics essential for excellent customer service and efficient operations. By minimizing delays inherent in complex relational database queries, it helps reduce service disruptions and enhances overall system performance.
Elasticsearch Features
The features of Elasticsearch are exposed as REST APIs, and they are as follows:
- Index API: The Index API allows you to document the index.
- Get API: The Get API allows you to retrieve the document.
- Search API: The Search API offers the ability to submit your query and receive a result.
- Put Mapping API: The Mapping API allows for the custom definition of mapping choices.
Elasticsearch has developed its own query domain language, enabling you to build queries in JSON. For more complex searches, it supports nested queries that accommodate various conditions, weights, thresholds, and predefined fields. Consequently, Elasticsearch's query language is well-suited for addressing the demands of practical search scenarios.
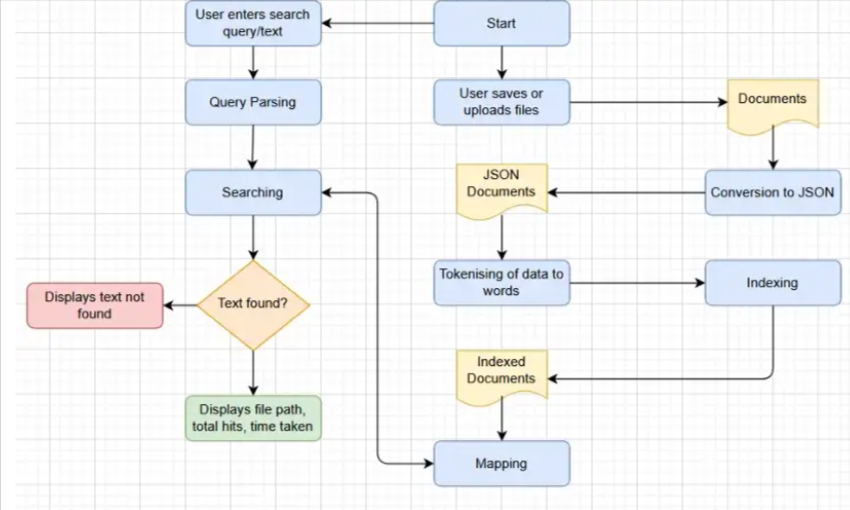
How Does Elasticsearch Query Work?
Please review the diagrams below, to understand briefly how Elasticsearch Query Works:
What Is Elasticsearch Used For?
- Text Search.
- Product Search.
- Data Aggregation.
- JSON Document Storage.
- Geo Search.
- Auto-Suggestion.
- Auto-Completion.
- Analytics.
- Security Analytics.
Primary Use Cases For Elasticsearch
- Application search: When using a search platform for data retrieval and reporting, applications need to be able to access, retrieve, and report data quickly.
- Website search: Elasticsearch’s popularity as a site search tool is steadily increasing. Websites find this open-source technology instrumental for accurate searches and effective data management.
- Enterprise search: Elasticsearch is a search engine that can be used to index virtually any kind of data and achieve enterprise-wide search capabilities, including documents and E-commerce products. It has become increasingly popular over the past few years and has even replaced the search solutions of many popular websites.
- Analytics: Elasticsearch is commonly used for ingesting and analyzing log data in near-real-time, scaling to support high volumes of log data. Elasticsearch also provides important operational insights on log metrics, enabling actions to be taken.
- Security analytics: The Elastic Stack (ELK), which includes Logstash, Kibana and Beats, can be used to analyze access logs and similar information concerning system security. This allows you to gain a more complete picture of what is happening across your systems in real-time.
Benefits Of Using Elasticsearch
- Faster Data retrieval: Data retrieval is quicker and more efficient when documents are stored near their corresponding metadata in the index. This reduces the number of data reads and as a result, increases search response time.
- Quicker Response: Elasticsearch, can fetch requested search query data in a fraction of the time it would take for a traditional SQL database management system.
- Scalability: Elasticsearch has a distributed architecture, which allows it to scale up to thousands of servers and accommodate petabytes of data. Scaling a workload across multiple nodes is easy. Start with fewer nodes and add more if needed, without incurring downtime. Customers then do not have to deal with the complexity of designing a distributed system, as that has already been done for them automatically.
- Multilingual: Elasticsearch supports multiple languages.
- Document Oriented: The data is stored in JSON format, instead of the database tables used in the old implementations. This change allows for easier integration into other applications if you need to share your results with a team or client who uses a different platform.
- Auto-completion: Elasticsearch allows for auto-completion of the search queries.
The Elastic Stack (ELK)
Elasticsearch is one of the core components of Elastic Stack, an open-source collection of tools for data ingestion, enrichment, storage, analysis and visualization. It was originally called the ELK stack after its component names Elasticsearch, Logstash and Kibana, but now also includes Beats. Although a search engine at its core, users started using Elasticsearch for log data and wanted a way to easily ingest and visualize that data.
Conclusion
Elasticsearch, a versatile search engine used for search and analytics, forms the core of a complementary tool ecosystem. This ecosystem addresses diverse use cases, including search, analytics, and data processing and storage.